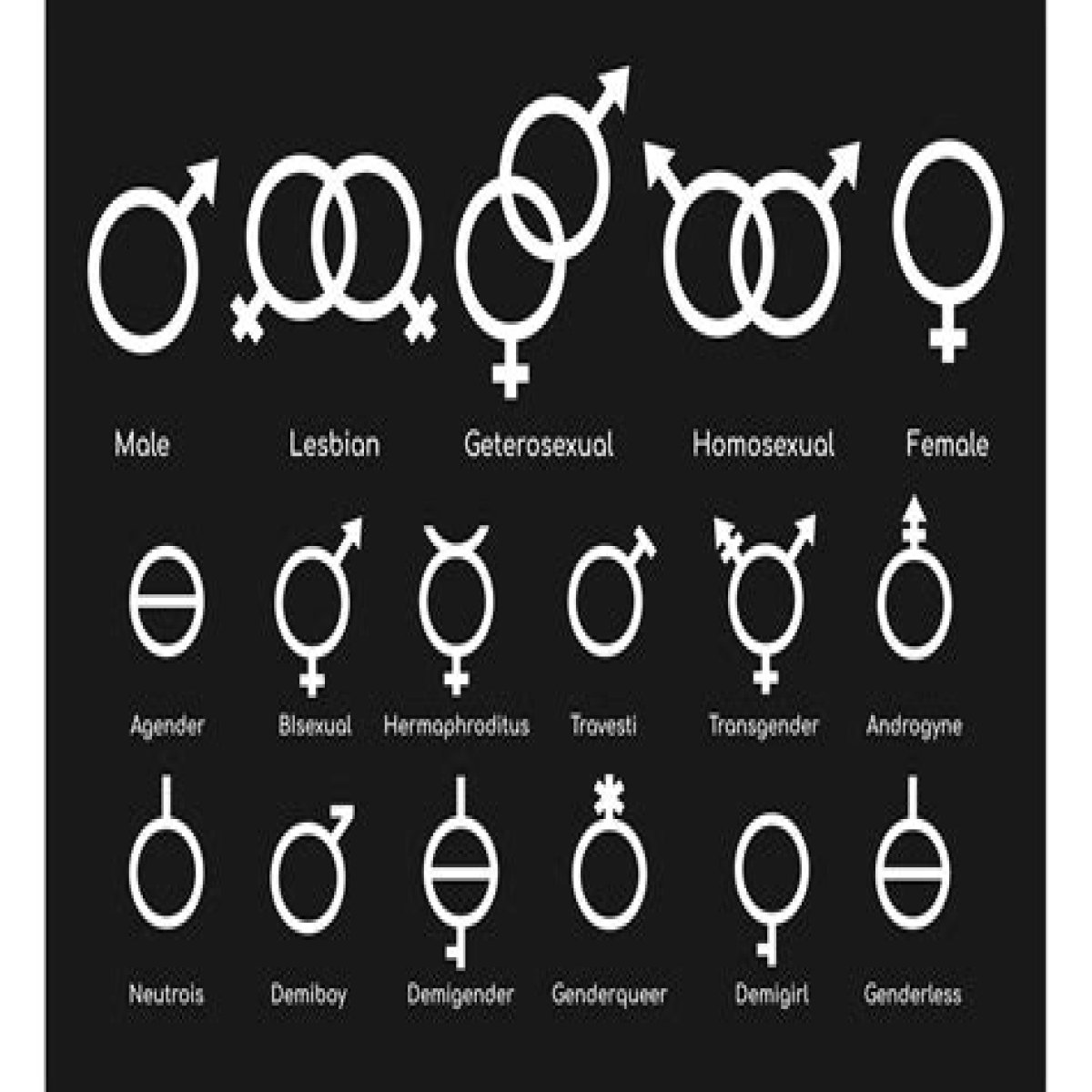
What is the significance of the male and female symbols?
The male and female symbols are two of the most recognizable symbols in the world. They are used to represent the biological sexes of humans and other animals. The male symbol is a circle with an arrow pointing up, while the female symbol is a circle with a cross below it.
These symbols have been used for centuries, and they have a variety of meanings and interpretations. In some cultures, they are seen as symbols of fertility and reproduction. In other cultures, they are seen as symbols of gender roles and social status. Today, these symbols are still widely used, and they continue to be a source of fascination and debate.
The male and female symbols are a powerful reminder of the diversity of human experience. They represent the different ways that people can express their gender and sexuality. These symbols are also a reminder of the importance of equality and respect for all people, regardless of their gender identity or sexual orientation.
Male vs Female Symbol
The male and female symbols are two of the most recognizable symbols in the world. They are used to represent the biological sexes of humans and other animals. The male symbol is a circle with an arrow pointing up, while the female symbol is a circle with a cross below it.
- Biological Representation: The symbols represent the biological differences between males and females, particularly in reproductive anatomy.
- Gender Identity: Beyond biological sex, the symbols can also represent gender identity, which may not always align with biological sex.
- Social Roles: Historically, the symbols have been used to denote social roles and expectations associated with masculinity and femininity.
- Cultural Symbolism: In various cultures, the symbols have acquired specific meanings and interpretations, often tied to fertility, procreation, and balance.
- Historical Evolution: The symbols have undergone changes in design and meaning over time, reflecting societal and cultural shifts.
- Modern Usage: Today, the symbols continue to be widely used in various contexts, including biology, healthcare, and gender studies.
- Equality and Respect: The symbols serve as a reminder of the diversity of human experience and the importance of equality and respect for all individuals.
These key aspects highlight the multifaceted nature of the male and female symbols. They represent not only biological distinctions but also social, cultural, and personal dimensions of gender. Understanding these aspects helps us appreciate the complexity and significance of these symbols in human societies.
Biological Representation
The male and female symbols are closely connected to their biological representation. They serve as visual representations of the distinct reproductive anatomies of males and females. The male symbol, with its upward arrow, is often associated with the penis, while the female symbol, with its cross, is associated with the vagina. These symbols provide a simplified and recognizable way to denote the biological sexes.
The biological representation of the male and female symbols is significant because it forms the basis for many social and cultural constructs around gender. In many societies, these symbols have been used to define gender roles and expectations, as well as to categorize individuals into male and female categories. Understanding the biological representation of these symbols helps us recognize the influence of biological factors on our understanding of gender.
However, it is important to note that the biological representation of the male and female symbols is not the only factor that determines gender identity or expression. Social, cultural, and personal factors also play a significant role in shaping how individuals identify and express their gender. Therefore, while the biological representation of the male and female symbols provides a basis for understanding the biological differences between males and females, it is only one aspect of a complex and multifaceted concept.
Gender Identity
The connection between gender identity and the male and female symbols is significant because it challenges the traditional binary view of gender. Traditionally, these symbols have been used to represent biological sex, which is assigned at birth based on external genitalia. However, gender identity is a more complex and personal experience that may not always align with biological sex. For many individuals, their gender identity does not fit neatly into the categories of male or female, and they may identify as non-binary, genderqueer, transgender, or another gender identity.
The male and female symbols can be used to represent gender identity in a variety of ways. Some individuals may choose to use the symbol that aligns with their biological sex, while others may choose to use the symbol that aligns with their gender identity. Still others may choose to use a different symbol altogether, such as the intersex symbol, which represents individuals who are born with variations in their sex characteristics. Ultimately, the choice of which symbol to use is a personal one, and there is no right or wrong answer.
Recognizing the connection between gender identity and the male and female symbols is important for promoting inclusivity and respect for all individuals. It helps us to understand that gender is not a binary concept, and that there is a wide range of gender identities and expressions. This understanding can help to create a more welcoming and supportive environment for everyone, regardless of their gender identity.
Social Roles
The male and female symbols have historically been used to represent not only biological sex but also social roles and expectations associated with masculinity and femininity. These symbols have been embedded in cultural norms and traditions, shaping how individuals are perceived and expected to behave.
- Gendered Occupations: The symbols have been used to designate occupations and professions as masculine or feminine. For example, jobs involving physical labor or leadership were often considered masculine, while jobs involving caregiving or education were considered feminine.
- Behavioral Expectations: The symbols have influenced societal expectations of behavior based on gender. Men were expected to be strong, assertive, and rational, while women were expected to be gentle, nurturing, and emotional.
- Social Status: In many cultures, the male symbol has been associated with higher social status and authority, while the female symbol has been associated with lower status and subordination.
- Division of Labor: The symbols have been used to justify the division of labor in society, with men primarily responsible for breadwinning and women responsible for domestic duties.
The connection between the male and female symbols and social roles has had a profound impact on individuals and societies. It has shaped gender stereotypes, influenced career choices, and perpetuated inequalities. However, in recent years, there has been a growing challenge to these traditional gender roles, and the symbols are increasingly being used to represent a more diverse and inclusive range of gender identities and expressions.
Cultural Symbolism
The male and female symbols have taken on specific meanings and interpretations in different cultures around the world. These meanings are often tied to fertility, procreation, and balance.
In ancient Egypt, the male symbol represented the god Osiris, who was associated with fertility and the underworld. The female symbol represented the goddess Isis, who was associated with motherhood and magic. Together, these symbols represented the balance between the masculine and feminine forces in the universe.
In Chinese culture, the male symbol represents yang, which is associated with the sky, light, and activity. The female symbol represents yin, which is associated with the earth, darkness, and receptivity. Together, these symbols represent the balance between the opposing forces in the universe.
In many Native American cultures, the male and female symbols are used to represent the duality of nature. The male symbol represents the sun, while the female symbol represents the moon. Together, these symbols represent the balance between the masculine and feminine forces in the natural world.
Understanding the cultural symbolism of the male and female symbols can help us to appreciate the diversity of human cultures and the different ways that people have conceptualized gender and the relationship between men and women.
Historical Evolution
The male and female symbols have not remained static throughout history but have evolved in design and meaning, reflecting the changing societal and cultural contexts in which they are used. This evolution sheds light on the dynamic nature of gender and its representation.
- Changing Gender Roles:
The symbols have adapted to reflect changing gender roles and expectations. For instance, during the feminist movement, the female symbol was reinterpreted to represent female empowerment and independence, deviating from traditional associations with passivity and domesticity.
- Cultural Influences:
Cultural exchanges and globalization have influenced the design and meaning of the symbols. The Venus symbol, commonly used to represent the female gender, originated from ancient Roman culture and has spread globally, becoming widely recognized.
- Artistic Interpretations:
Artists and designers have played a role in shaping the visual representation of the symbols. Contemporary art often challenges traditional depictions, offering diverse and thought-provoking interpretations that reflect evolving societal attitudes towards gender.
- Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements have impacted the use andof the symbols. The symbols have been adapted for digital communication, leading to new interpretations and variations, such as emojis and gender-inclusive symbols.
The historical evolution of the male and female symbols underscores the close relationship between gender and culture. The symbols are not merely static representations but evolve alongside societal and cultural shifts, reflecting our changing understandings and perceptions of gender.
Modern Usage
The male and female symbols continue to be widely used in modern society, serving various purposes across different fields.
- Biology:
In biology, the symbols are used to denote the sex of organisms, indicating their reproductive roles and genetic makeup. Biologists use these symbols to classify and study species, understand genetic inheritance, and analyze reproductive patterns.
- Healthcare:
In healthcare, the symbols are employed to identify the sex of patients, guide medical treatments, and communicate health information. They are used on medical charts, prescriptions, and patient records to ensure accurate and efficient healthcare delivery.
- Gender Studies:
In gender studies, the symbols are used to represent and analyze gender identities, roles, and relationships. Researchers and scholars utilize these symbols to explore the social and cultural construction of gender, examine gender equality, and advocate for gender inclusivity.
The continued use of the male and female symbols in these contexts highlights their enduring relevance in representing and understanding biological sex, gender identity, and healthcare needs. These symbols provide a common language for communication and enable researchers, healthcare professionals, and individuals to engage in informed discussions and decision-making related to sex and gender.
Equality and Respect
The male and female symbols carry significant implications for equality and respect, highlighting the diversity of human experiences and the need for inclusivity. These symbols represent more than just biological distinctions; they encompass social, cultural, and personal dimensions of gender identity.
- Embracing Diversity:
The symbols remind us that gender is not a binary concept, but rather a spectrum of identities and expressions. They encourage us to recognize and respect the diverse ways in which individuals identify and express their gender, fostering an inclusive society that values all genders.
- Challenging Stereotypes:
By challenging traditional gender roles and stereotypes, the symbols promote a more nuanced understanding of masculinity and femininity. They encourage us to move beyond limiting societal expectations and embrace a broader range of gender expressions, breaking down barriers and creating a more equitable world.
- Promoting Inclusivity:
The symbols serve as a reminder of the importance of inclusivity and equal rights for all individuals, regardless of their gender identity or expression. They advocate for policies and practices that ensure fair treatment, equal opportunities, and a safe and respectful environment for everyone.
- Respect for Human Rights:
The symbols embody the fundamental principles of human rights, emphasizing the inherent dignity and equality of all human beings. They remind us that every individual deserves to be treated with respect and compassion, regardless of their gender identity or expression, and that discrimination based on gender is unacceptable.
In conclusion, the male and female symbols serve as powerful reminders of the importance of equality and respect for all individuals. They encourage us to embrace diversity, challenge stereotypes, promote inclusivity, and uphold human rights. By fostering a society that values and respects all genders, we create a more just and equitable world for everyone.
FAQs on Male vs Female Symbol
The male and female symbols are widely recognized and carry various meanings and interpretations. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions surrounding these symbols:
Question 1: What is the origin of the male and female symbols?
The exact origin of the symbols is unknown, but they have been used for centuries in various cultures. The male symbol, representing the planet Mars, and the female symbol, representing the planet Venus, have roots in ancient astrology and alchemy.
Question 2: What do the male and female symbols represent?
Primarily, the symbols represent the biological sexes of humans and animals. However, they have also been used to represent gender identity, social roles, and cultural concepts related to masculinity and femininity.
Question 3: How are the symbols used in modern society?
The symbols are commonly used in biology, healthcare, and gender studies. They are also found on public restrooms, locker rooms, and other places where it is necessary to designate separate facilities for males and females.
Question 4: What is the difference between sex and gender?
Sex typically refers to the biological and physiological characteristics that define a person as male or female. Gender, on the other hand, refers to the social and cultural roles, behaviors, and identities associated with being male or female.
Question 5: Why is it important to respect gender diversity?
Recognizing and respecting gender diversity is crucial for creating an inclusive and equitable society. It involves understanding and valuing the diverse ways in which individuals identify and express their gender, regardless of their biological sex.
Question 6: How can we promote gender equality?
Promoting gender equality requires challenging stereotypes, fostering inclusive environments, and advocating for policies and practices that ensure equal opportunities and rights for all individuals.
In summary, the male and female symbols have a long history and are used in various contexts to represent biological sex, gender identity, and social roles. Recognizing the distinction between sex and gender, respecting gender diversity, and promoting gender equality are essential for building a more inclusive and just society.
Transition to the next article section:
The significance of the male and female symbols extends beyond their representation of biological sex and gender roles. These symbols carry cultural meanings and have been influential in shaping societal norms and expectations. Understanding the historical and cultural context of these symbols provides a deeper appreciation for their multifaceted nature and the role they play in our societies.
Conclusion
The male and female symbols are powerful and multifaceted symbols that have shaped human societies for centuries. They represent not only biological sex but also gender identity, social roles, and cultural beliefs. Understanding the history, cultural significance, and evolving nature of these symbols provides a deeper appreciation for the complexity of gender and its representation.
As we move forward, it is crucial to recognize and embrace the diversity of gender identities and expressions. By challenging stereotypes, promoting inclusivity, and advocating for equality, we can create a more just and equitable world for all individuals, regardless of their gender.